
Schizophrenia is a highly disabling mental disorder, and numerous studies have shown that the hypofunction of the N-methyl-
In a study published in Cell on March 20, a research team led by Prof. ZHAO Yan from the Institute of Biophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has revealed three different conformations of the full-length wild-type human GlyT1 transporter, firstly providing the elucidation of substrate recognition and the mechanism by which three anti-schizophrenia drug candidates selectively inhibit GlyT1.
The researchers reported the structure of GlyT1 with glycine bound in an occluded state, while identifying the binding sites of a chloride ion and two sodium ions that were co-transported with glycine, elucidating the coupling mechanism of substrate and ion binding during transport.
Currently, clinical candidate drugs targeting GlyT1 for the treatment of schizophrenia can be divided into sarcosine-based and non-sarcosine-based classes. The researchers found that the initial lead sarcosine-based inhibitor, ALX-5407, binds to an inward pocket of GlyT1. They also identified the first patented non-sarcosine-based inhibitor SSR504734, and the drug PF-03463275, which is currently in Phase II clinical trials, to bind to an outward pocket of GlyT1.
This study explores the substrate recognition, ion binding, conformational transition of GlyT1, and the structure-activity relationships with the clinical trial drugs. It will help accelerate the drug development process targeting GlyT1, providing strong theoretical support for the design and development of anti-schizophrenia drugs.
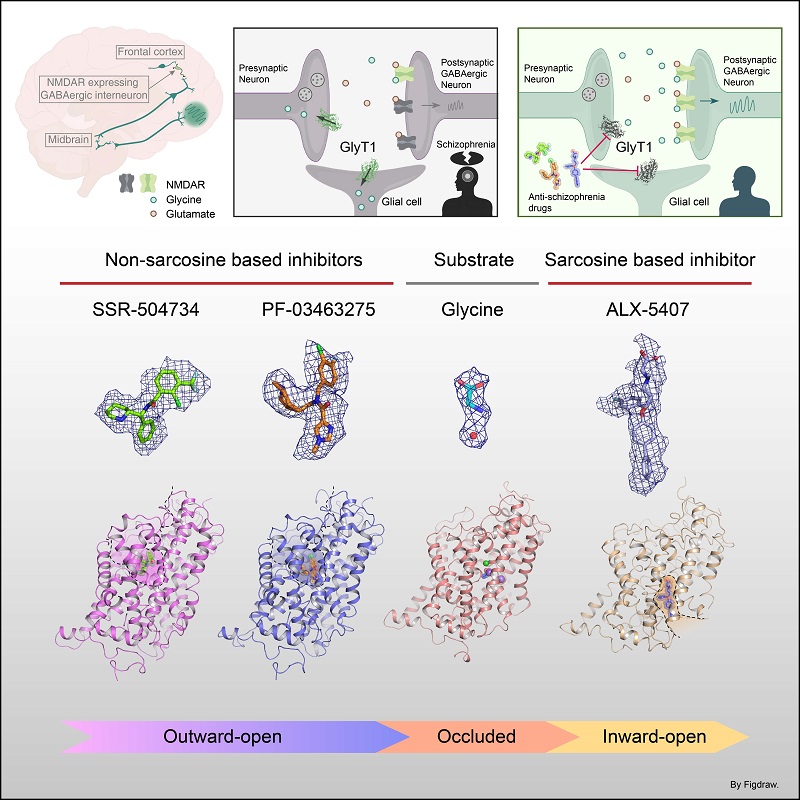
The molecular mechanisms of GlyT1 in physiology and pharmacology. (Image by ZHAO Yan's group)

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

86-10-68511095 (day)
86-10-68512458 (night)

cas_en@cas.cn

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

